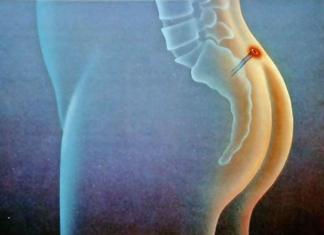
Inflammation of the sciatic nerve (sciatica) can occur unexpectedly even in people who consider themselves healthy. The sciatic nerve is the longest in the human body. It begins in the lumbar region, passes through the tailbone, the back of the pelvis and both lower limbs, reaches the feet. Therefore, pain and sensory impairment with sciatica affects not only the lumbar region, but also spreads to the legs along the entire nerve.
Inflammation itself is not a separate disease and usually serves as a manifestation of another pathology.
Causes of sciatica
The most common cause of sciatica is pinching of the sciatic nerve by spinal structures due to some pathological process in them.- Complete or partial displacement of the intervertebral disc, accompanied by pinching of the sciatic nerve, narrowing of the spinal canal, growths on the spine;
- Piriformis syndrome;
- Damage to organs or the muscular system of the pelvis due to injury or heavy physical exertion;
- Hypothermia, infectious processes;
- Presence of neoplasms.
Symptoms of inflammation of the sciatic nerve
The main symptom of this condition is pain in the area of the sciatic nerve. As a rule, it is localized on one side of the body, and on the opposite side There is numbness in the corresponding area, which is periodically replaced by tingling. But it happens that both legs are involved in the process at the same time.
The intensity of pain may vary. At the beginning of inflammation, they are mild and intensify with physical activity, sneezing, and laughter. As the disorder develops, the unpleasant sensations increase and are constantly present, becoming especially intense at night. The patient may wake up from attacks. In severe cases, the patient cannot move due to severe pain.
Diagnostics
If symptoms appear, you should consult a neurologist. The doctor will conduct a general examination. With sciatica, there may be decreased mobility of the joints of the knees or feet, weakened or abnormal neurological reflexes, and increased pain when trying to lift a straight leg upward.
A general and biochemical blood test, x-rays taken in different projections in a standing and lying position, and magnetic resonance imaging will help confirm the diagnosis. Sometimes you may need to additionally visit another specialist - a rheumatologist, vascular surgeon, or vertebrologist.
Urgent consultation with a doctor is required if:
- Against the background of pain, body temperature rises to 38 o C;
- Swelling or reddened skin appears on the back;
- The pain gradually spreads to new areas of the body;
- There is severe numbness in the pelvic area, hips, legs, making it difficult to walk;
- There is a burning sensation when urinating, and there are problems with holding urine and feces.
Treatment of sciatica
The set of procedures is selected differently for each patient and depends on the specific symptoms and severity of the condition. It includes:
- Mode. During the period of acute pain, the patient needs to lie on a bed with a hard mattress, and also limit physical activity until the inflammation subsides;
- Medicines. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, and vitamins are used. Ointments and gels of irritating action are applied topically to relieve pain and reduce spastic syndrome;
- Physiotherapy. Warming compresses, heating, electro- or phonophoresis are prescribed. When used in combination medicines(antispasmodics, anti-inflammatory, muscle relaxants, vitamins) with physiotherapy, their effect increases significantly;
- Massage. They begin after the acute process has subsided. It helps reduce pain, increases the conductivity of the damaged nerve, improves blood supply and lymph flow, and prevents muscle wasting;
- Physiotherapy. After determining the cause of inflammation of the sciatic nerve, an exercise program is individually selected for the patient. Some of them need to be performed already in the first days of illness, while lying in bed. As motor activity is restored, the load is gradually increased. Activities in the pool are also recommended. Water reduces pain, relieves muscle spasms, facilitates movement;
- Surgical treatment. Indicated in cases where conservative methods do not work and the severe pain syndrome becomes chronic, as well as in severe disorders of the pelvic organs.
Prevention
 In the subacute period of the disease, one of the effective therapeutic measures is a massage.
In the subacute period of the disease, one of the effective therapeutic measures is a massage. To prevent inflammation of the sciatic nerve, it is necessary to pay attention to maintaining the tone of the back muscles. You should practice and monitor correct posture. When working sedentarily, take regular breaks and stretch.
It is necessary to avoid injuries, do not lift heavy objects and avoid hypothermia. It is also necessary to contact specialists in time to treat pathologies that cause sciatica.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you have inflammation of the sciatic nerve, you should consult a neurologist. Additionally, you may need to consult a neurosurgeon, vertebrologist (for diseases of the spine), vascular surgeon (for differential diagnosis with damage to the vessels of the limb). The treatment also involves a physiotherapist, a specialist in physical therapy and massage, you can also contact an osteopath.
Video version of the article:
About sciatica in the program “Live Healthy!” with Elena Malysheva:
In the “Health” program with Elena Malysheva about paralytic sciatica syndrome:
The sciatic nerve is considered the largest in the human body, because of this it can become inflamed more often than others. This nerve begins from the pelvic area in the lumbar region, and then it passes through the pelvis, goes under the gluteal muscle and branches and passes through almost all the femoral and gluteal muscles.
Sciatic nerve entrapment
When the sciatic nerve is pinched, the first thing that occurs is pain, which can be of different types, for example, shooting, stabbing, pulling. In this case, the pain is paroxysmal and severe, followed by periods of rest. Pain sensations arise in the lumbar region, and go from top to bottom, spreading almost to the very toes. Moreover, pain can even occur in both legs at once. But most often, there is still pain, only in one leg, and the second leg goes numb, perhaps a feeling of tingling and goosebumps. In especially severe cases, the pain may be so severe that the person cannot even make any movements.

The causes of this pathology are as follows::
- General hypothermia of the body. And especially hypothermia of the lumbar region, which can occur even in the warm season. For example, when the lumbar region is blown by a cold wind.
- Heavy physical activity associated with lifting weights, which can result in deformation of the muscle frame and, as a result, pinching of the sciatic nerve. A sudden and awkward movement, especially in the lumbar region, can also contribute to the formation of this pathology.
- Osteochondrosis can also contribute to a pinched nerve. Herniated discs can also lead to nerve problems. Other diseases, such as diabetes and various tumors, can also contribute to this.
Piriformis syndrome causes problems with the sciatic nerve; if the muscle is tense, the sciatic and pudendal nerves are compressed and pain occurs; nerve entrapment is also possible during pregnancy.
Sciatic nerve: how to treat
First of all, treatment is aimed at eliminating pain syndromes; for this purpose, a variety of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. After pain relief, you can directly treat the cause of the disease.
Treatment for this disease is as follows:
- A variety of UHF physiotherapeutic procedures, magnetic therapy, electrophoresis and other procedures. During treatment, various fixing belts are used, muscles are stimulated with electrical impulses and manual therapy is used.
- If the pinching of this nerve was caused by a hernia or any tumor, then in this case, after stopping pain syndrome An operation is prescribed to eliminate the cause of the pinched nerve.
- If the sciatic nerve has been pinched due to infection, you should treat the disease by taking antibiotics and antibacterial drugs. In this case, it is advisable to observe bed rest until almost complete recovery.
But in the event of an attack, it is not always possible for a person to immediately come to a medical facility or see a doctor.
In this case, a person, independently or with someone’s help, needs to lie on his stomach on a hard surface, placing a pillow or a rolled blanket under his chest.
You can cover yourself with a blanket on top. You should not apply any ointments or creams or apply heating pads to the sore spot, as this can only worsen the situation. Afterwards, all that remains is to wait for qualified medical assistance.
Symptoms: sciatic nerve
Symptoms of sciatic nerve entrapment are difficult to miss. First of all, this is pain in the buttock and thigh area, and the pain can be quite intense and paroxysmal. Pain sensations spread from bottom to top. Sometimes the pain is so intense that it is difficult for a person to straighten up, turn around, and when trying to take a step, the person experiences very sharp pain in the left or right leg, depending on which side of the body the nerve is pinched. But sometimes the pain can feel like tingling, numbness it all depends on individual characteristics body.
Signs:
- The very first signs of this disease are slight pain in the lower back in the gluteal muscle; fatigue in the leg muscles may be observed with a relatively small load. Gradually the disease progresses, and the pain begins to radiate from the thigh, lower leg to the foot.
- Less commonly, problems arise with two sciatic nerves at once, with pain radiating to the hips, knees, and even feet. In this case, pain may intensify when lifting heavy objects, walking for long periods of time, and even when sitting.
- Sometimes there may be impaired mobility of the limbs or in the knee and ankle joint. Examination may reveal abnormal or weakened reflexes, decreased sensitivity, and even partial muscle atrophy.
In some cases, a person may experience urinary and fecal incontinence, but this is usually the exception rather than the rule. There may be a slight increase in temperature, redness of the skin in the affected area and slight swelling.
Femoral nerve
The femoral nerve is most often affected in the area where it exits the thigh from the retroperitoneum. After exiting, this nerve is divided into subcutaneous, motor and muscular sections (motor sections). When it is affected, pain or numbness is observed in the area of the anterior inner thigh.
Other symptoms may also occur if there are problems associated with this nerve.:
- Weakness of the muscles in the leg, a person may have a feeling that the limb does not obey, as if it is becoming “foreign”, bends and barely moves, there may be a sensation of electric current passing through the limb.
- When straightening the leg, pain occurs, which intensifies when straightening the limb, and a decrease in sensitivity is also observed. When examined by a doctor, a decrease in the knee reflex may be noted.
- Also, when examined by a doctor, pain is detected along the anterior inner surface of the thigh, muscle weakness and, in some cases, partial atrophy of the leg muscles.
Most often, this disease occurs in women and only occasionally in men over the age of 40; to clarify the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes MRI, ultrasound and other necessary studies prescribed by the doctor. After diagnosis, treatment is prescribed - primarily analgesics and decongestants. For pain, blockades are prescribed, and exercise therapy is used for treatment. In extreme cases, surgical intervention in the area of the inguinal ligament is prescribed.
How to treat a pinched sciatic nerve
Most often, treatment of this disease is performed by a neurologist. First of all, painkillers are prescribed, most often injections and bed rest for several days.

If a person has a very painful posterior pinched nerve, then pain blockades are performed.
In addition, injections are given with drugs that improve blood circulation, and massage is also prescribed using warming and anti-inflammatory drugs outside the period of exacerbation. The use of such ointments is used as an aid.
In order to cure these diseases, the following methods should be used:
- Magnetotherapy, the effect of a magnetic field on the affected area, which allows you to relieve swelling and spasm and improve blood flow in the affected area. After this, the person can say: I sit without pain.
- Paraffin applications are also prescribed; due to the effect of heat, muscles relax, blood flow improves, and lymph drainage also increases, which reduces swelling and improves metabolic processes.
- Physiotherapy is used, in particular electrophoresis with the use of drugs, exercise therapy, massage, and drugs that improve metabolic processes are prescribed. Thanks to this, metabolic processes and blood circulation improve.
Some people use a variety traditional methods, for example, rub the sore spot with tincture of pine needles, or tincture of coniferous cones.
Massage for pinched sciatic nerve (video)
So, sometimes, due to this pathology, there may be a feeling that someone is pulling the right or left leg, or the pain may be wandering. In any case, you should seek medical help. Treatment is mandatory.
Part of the sacral plexus, the sciatic nerve is the largest in the human body. It is located along the entire length of the leg, starting from the tailbone and ending with the foot. If pain occurs in the lower limb, a person may suspect pinching of the sciatic nerve.

Compression of the sciatic nerve without disruption of the myelin sheath is a pathological process accompanied by a pain syndrome called pinching. The location is the lumen of the sciatic foramen in the area of the piriformis muscle or vertebral discs.
Most often, pinching of the sciatic nerve occurs in one limb, but there are cases when two legs are affected. The condition may be complicated by intense pain and inflammation of the sciatic nerve, in medical practice called sciatica.
Strong pain in the buttock area, radiating to the leg - one of the common symptoms of sciatica, which can be aggravated by inflammation of the piriformis muscle. Manifestations of the disease may be similar to osteochondrosis and other pathologies, differentiate pinching of the sciatic nerve and prescribe correct treatment Only a qualified doctor can.
Main causes of pathology
- Intervertebral hernia is one of the main causes of pathology. Degenerative changes intervertebral discs, accompanied by rupture of the fibrous ring and displacement of the nucleus pulposus, can cause pinching of the nerve roots.
- Traumatic impact on the spinal column with displacement of the vertebrae.
- Osteochondrosis in the lumbar and sacral region.
- Neoplasms of various types in the area of the sciatic nerve.
- Excessive physical activity associated with heavy lifting.
- Inflammation of organs located in the pelvis.
- An abscess localized in the area of the sciatic nerve.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Infectious diseases: bone tuberculosis, malaria, rubella and others.
- Changes in blood vessels with the formation of blood clots.
- Exposure to cold air in the area lumbar region.
- Muscle inflammation in the buttock area.
- The condition of pregnancy can cause the disease. As a result of the enlargement of the fetus, the uterus puts pressure on neighboring organs and tissues, causing pinching of the nerve column.
In addition to preexisting conditions that may affect the sciatic nerve, there are a number of risk factors:
- obesity;
- lack of minerals in the body;
- poisoning with salts of heavy metals, ethanol derivatives;
- herpetic herpes zoster in the area of the sciatic nerve.
Symptoms

The main symptom of the disease is a nagging pain along the nerve fiber. The pain can be sharp, aching, shooting, of varying intensity, affecting the back surface of the buttock, thighs, and going down to the knee and ankle joint.
Increased pain can be caused by a change in body position in a sitting position, cough reflex, or during laughter. Unpleasant sensations of tingling, numbness and burning of the skin are observed in the area of the sciatic nerve. It becomes difficult for the patient to stand for a long time, the person begins to limp, falling on the affected leg.
In addition to the characteristic pain, there are additional symptoms:
- sudden shooting pain in the lumbar region, radiating along the entire length of the lower limb to the heel;
- feeling of slight stabbing pain on skin sore legs that appear between attacks of pain;
- the back surface of the thigh and buttocks “burns”, reminiscent of the sensations after thermal exposure;
- with large areas of damage, the upper layers of the skin lose their sensitivity and become numb;
- limited movement of the legs and lumbar spine;
- muscle weakness in the affected leg;
- increased symptoms when moving to a sitting position.
Women experience lower back pain less frequently than men. Infringement of the sciatic nerve in the male half resembles prostatitis in its manifestations with unpleasant sensations in the pelvic area.
Diagnostics

To make a correct diagnosis, consultation with an experienced specialist is required. At first glance, it may seem that, due to the specific pain characteristic of neurological pathology, any patient can diagnose a pinched sciatic nerve.
However, in some cases clinical picture the disease is similar to destructive changes in the spinal discs that form intervertebral hernia. Hernia pain is more prolonged, acute, and has a greater risk of recurrence of neurological pain.
The examination by a doctor consists of several stages:
- collecting anamnesis includes studying the patient’s complaints about the objective nature of the symptoms and their intensity;
- visual inspection and palpation of the affected area;
- diagnostic research methods prescribed by a doctor to collect a complete picture of the pathology.
The methods of accurate diagnosis are as follows.
- X-ray of the lumbar and pelvic area.
- Ultrasound examination of the affected area.
- Computed and magnetic resonance tomography.
- Study of muscles and peripheral nerve fibers using responses to electrical impulses.
- If a malignant formation is suspected, a radioisotope scan of the spinal column is performed.
- General analysis and blood biochemistry.
The final diagnosis will be helped by specific symptoms for pinched sciatic nerve:
- Bonnet's symptom: increased pain when raising the limb upward and decreased pain when bending the leg at the knee, all actions are performed by a doctor;
- Lasegue's symptom: the patient, lying on his back, raises his straight leg up, experiencing pain, and slowly bends the limb at the knee, and the pain becomes almost imperceptible;
- cross syndrome consists of feeling pain in both legs when lifting the affected limb;
- decreased plantar, knee and Achilles reflexes.
Treatment of pinched sciatic nerve
How to treat a pinched sciatic nerve? After confirming the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes an effective complex treatment aimed at eliminating the pathological process. Blocking pain is one of the main directions of therapeutic procedures. The key to complete victory over the disease is to eliminate the cause of pinching of the largest nerve in the lower part of the human body.
Therapy consists of a medication component, physiotherapy, alternative medicine, orthopedic regimen using warming bandages and corsets varying degrees rigidity.
Therapeutic procedures at home

Many patients, feeling unbearable, begin self-treatment Houses. Using recipes and advice from traditional healers, patients do not always achieve the desired result. Often, falling into the hands of charlatans without medical education, you can acquire a lot of complications that lead to irreversible consequences for human health.
Therefore, deciding to therapeutic effect at home, you must comply important condition: any action must be coordinated with the attending physician so as not to harm the body.
Frequent therapeutic manipulations carried out by patients at home are as follows.
- You can rub your sore leg alcohol solution, pre-cooked. Spruce or pine buds, pine needles or coltsfoot flowers must be poured with alcohol in a ratio of 1:1 by volume, placed in a dark place and allowed to brew for a week. The tincture has an anti-inflammatory and moderate analgesic effect on the sciatic nerve.
- Massage using warming analgesic ointments requires mandatory consultation with a doctor, especially in the acute period of pathology. Massage cupping should be used with extreme caution so as not to aggravate the situation.
- Wax applications to the affected area are applied to skin previously lubricated with a rich cream. Wax deeply warms the skin and can cause an increase in the inflammatory response when the sciatic nerve is pinched.
- Gymnastic exercises during the recovery period of pathology have a beneficial effect on joints. A specially selected set of exercises, developed individually for a particular patient, will be effective. Only a physiotherapist can create a list of exercises.
We can conclude that treatment at home will not lead to the desired result; such measures will not be sufficient for a complete cure. Temporary improvement can be an insidious deception, followed by a relapse.
Medical tactics
The complex of therapeutic measures includes medicinal procedures and physiotherapeutic effects on the sciatic nerve. Symptomatic treatment consists of relieving pain to alleviate the patient's suffering. To eliminate neurological pain, a blockade with the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is prescribed; for mild pain, it is enough oral administration analgesics.
If the pinching is caused by an inflammatory muscle lesion, the doctor prescribes muscle relaxants that relax the muscle fibers, and antispasmodics. Venotonics will help improve blood circulation in affected tissues. In addition, reception vitamin complexes promotes rapid recovery of the patient's body. Warming and analgesic ointments will have a local effect, helping to cope with pain.
Physiotherapeutic procedures included in the therapeutic complex:
- magnetic therapy, provided there are no contraindications, in particular the presence of malignant neoplasms;
- electrophoresis;
- applications with paraffin;
- treatment with medicinal leeches;
- hydrogen sulfide and mud baths;
- ultraviolet exposure to the area of the sciatic nerve;
- laser procedures.
Methods such as manual therapy, acupuncture, massage active points, must be agreed with a doctor to avoid worsening the condition. During the acute period of the disease, massage and manual manipulation are not recommended.
An orthopedic regime using a hard mattress and a corset for the lumbosacral spine, which acts sparingly, relieves the load on the diseased area. In case of severe pain, a rigid fixation corset is prescribed, which will help effectively eliminate the pain syndrome. In the future, the patient can use a corset for dynamic loads, which helps protect the vertebrae from heavy physical activity.
Prognosis and possible negative consequences
Seeing a doctor at the initial stage of the disease predicts a complete cure without negative consequences. The treatment prescribed by the doctor will completely restore all functions associated with the influence of the sciatic nerve.
Self-medication, the protracted nature of pinching of the sciatic nerve leads to the following changes:
- severe pain that is difficult to relieve;
- paralysis or partial immobilization;
- insomnia;
- disruption of the functionality of internal organs;
- violation menstrual cycle, in more severe cases - infertility;
- constipation and delayed bladder emptying;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases.
Prevention
Preventative measures to promote sciatic nerve health include:
- avoiding strenuous physical activity, particularly heavy lifting;
- hypothermia;
- preventing the appearance of extra pounds;
- balanced diet;
- avoid sudden turns of the body;
- lead an active lifestyle.
Conclusion
If you experience pain in the lower back, radiating to the leg, changes in gait and joint mobility, you should immediately consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis. “Blind” treatment using the selection method can only aggravate the pathological process and lead to complicated conditions that cannot be restored.
The hip joint is one of the largest joints in the human skeletal system, pathologies of which lead to disruption of many functions and greatly impair the quality of life. Pinched nerve in hip joint- this is its compression by muscle or ligament cords, neoplasms, displaced and damaged tissues, due to one reason or another. This pathology manifests itself as acute pain in the buttocks, hips and lower back.
Why pinching occurs
The main reasons are the following:
- Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine is a degenerative process that causes destruction of cartilage and bone tissue, with protrusion of discs and hernias that compress the nerve roots in the place where they exit the spinal cord canal.
- Inflammation of the piriformis muscle, which happens under heavy load - long walking or running, jumping, in people unaccustomed to sports, as well as when they are in an uncomfortable position for a long time and during hypothermia - spasm of the piriformis muscle pinches the sciatic nerve.
- The nerve is also infringed by tumor formations.

The formation of sciatic nerve pinching in the hip joint is influenced by a number of provoking factors:
- Excess weight and sedentary lifestyle;
- Joint diseases and bone pathologies;
- Injuries and inflammations of the hip joint and organs in this area;
- Severe colds;
- Hereditary predisposition, which largely determines the anatomical features of the location of the neurovascular bundles and ligamentous apparatus, as well as congenital defects of the articular apparatus, for example, hip dysplasia.
Separately, it is worth noting such a cause of pinching of the sciatic nerve in the hip joint as pregnancy. An increase in the load on a woman’s body, caused by an enlarging uterus, putting pressure on many organs and nerve bundles, careless movement can provoke pinching. Pregnancy also increases the load on the spine, which can also cause nerve pinching. This can also occur with postpartum divergence of the pelvic bones.

Clinical picture
Among the symptoms of pinching of the sciatic nerve in the hip joint, the main one is sharp, acute pain in the lumbar region radiating to the thigh and buttock. The intensity of the pain makes it impossible to move, bend, walk, or perform other leg movements.
In addition to pain, patients also indicate the following list of symptoms:
- Limitation of the range of motion of the hip joint.
- Paresthesia is a feeling of tingling and burning at the site of the lesion.
- Numbness at the site of injury.
- In some cases, fever, chills, sweating, and weakness occur.
The transmission of pain to the leg or back is called sciatica and is quite common in patients with pinched sciatic nerves, especially when trying to change position - stand up or lie down, or during physical activity.

How is diagnostics carried out?
Typical patient complaints of pain and its return, paresthesia and associated symptoms usually facilitate the diagnosis of a pinched nerve in the hip area. In addition, the doctor collects anamnesis and prescribes visual and laboratory diagnostic methods to confirm the diagnosis and select subsequent treatment:
- CT, MRI of the spine and soft tissues;
- X-ray of the pelvic bones and spine;
- Ultrasound of the hip joint;
- Electromyography;
- General and biochemical tests blood, general analysis urine.
Pinching treatment
It is necessary to treat this pathology; in an advanced state, the symptoms worsen and spread over a large area of the affected area. A neurologist or therapist should treat a pinched nerve in the hip joint.
Treatment in some cases is conservative and includes a set of methods:
- Pain relief, with the prescription of a course of analgesic drugs, including analgin, novocaine, ketorol and others. These drugs are administered intramuscularly at the beginning of treatment, then the patient is transferred to oral administration.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are drugs that relieve inflammation, pain and swelling. These include diclofenac, indomethacin, nimesulide, ketoprofen, movalis and others. They are prescribed by injection during the first days of therapy, after which they are taken orally in tablet form. The same drugs can be used topically, in the form of ointments and creams applied to the hip area.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures, these include hardware treatment methods, such as: electro- and phonophoresis, magnetic therapy, UHF, laser, diadynamic currents, also hot baths, wraps, paraffin applications, splinting and massage. Massage in the category of physiotherapeutic procedures is quite popular among prescriptions, as it is highly effective in relieving pinched nerves, and the combination of massage actions with locally acting products containing bee products and snake venom speeds up recovery. At the same time, massage and all types of manual therapy require the supervision of a doctor in order to avoid complications, and are carried out when acute phenomena subside.
- Physiotherapy. It begins with a set of exercises lying down while the patient is in bed - flexion-extension of the legs at the hip and knee joint, abduction-adduction of the leg at the joint, rotation of the leg. As the patient recovers, he can perform exercises while standing, strengthening the muscular frame of the back. These include squats and bends. All exercises must be carried out under the supervision of an instructor, at least for the first time.
Treatment of joints Read more >>
- Hormonal drugs. If there is no effect from other medications and physical therapy, the doctor may prescribe a course of drugs containing hormones.
- Methods of oriental medicine. In the treatment of neurological diseases, alternative treatment approaches show high effectiveness and can be prescribed along with other methods. These include acupuncture, stone therapy, hirudotherapy and manual therapy techniques. The principle of their work is to influence the active zones of the body, which stimulates blood circulation in the affected area, eliminates congestion, relieves pain and inflammatory processes.
- Folk remedies. At home, pinching in the hip joint is treated with baths with decoctions of medicinal plants - thyme leaves, calamus roots, oak bark. You can also take oregano decoctions internally, horse chestnut and chamomile. It is also recommended that home remedies include a mixture of ground walnuts, sunflower seeds, dried apricots and prunes - these products have a beneficial effect on the joint system. However, treatment for pinching at home should be complementary to the main course of medical prescriptions, and not independent.
- Daily routine and diet. Patients with acute pain must observe strict bed rest during the first days of the disease; after 2-3 days they are allowed to get out of bed, move within the room, and after a week - go outside. The bed is recommended to be flat and hard to avoid displacement of the vertebrae. The sleeping position should be on your side or back, with a small pillow placed under your shin. The pillow under your head should be low.
The diet of such patients involves the exclusion of salty, spicy, smoked foods. The diet should include vegetables, fruits, stewed and boiled meat, water-based porridge, and low-fat soups.

If the process is running, it may be shown surgery when surgery is performed to remove tissue pressing on the sciatic nerve.
Treatment of a pinched nerve during pregnancy occurs with the same symptoms, but treatment is prescribed taking into account the woman’s condition and excludes drugs with a negative effect on the fetus. As a rule, local anti-inflammatory drugs are used, for example, Voltaren, Menovazin ointments, compresses in the lumbar region, gentle massage and light gymnastic exercises.
More details
During pregnancy, surgical interventions are usually not performed, since this condition is most often temporary, it can be alleviated by gentle conservative therapy and after childbirth it goes away.
To exclude recurrences of a pinched nerve, it is necessary to treat the main cause that caused the disease - hernia, osteochondrosis, remove excess weight, regularly engage in appropriate physical activity, and avoid a sedentary lifestyle and sedentary state.
The sciatic nerve rarely bothers people, so many don’t even know what it is. In fact, it is the largest nerve in the human body, which is why it requires serious attention. Sciatic nerve pain, also called sciatica, can almost instantly seriously limit a person’s mobility.
A separate question is where the sciatic nerve hurts. The fact is that with sciatica, pain is felt approximately equally in the lower back and in the leg. A characteristic feature is the fact that pain almost always appears in only one nerve and is of a “shooting” nature. In addition, there may be sensory disturbances in the leg, a crawling or burning sensation.
Why does the sciatic nerve hurt?
The most common cause of sciatica is a herniated disc. We will not delve into the processes that occur during the formation of such a hernia (in this case, in the lumbar region), the only important thing is the fact that compression of the nerve roots occurs. It is this compression of the nerve that leads to the appearance of neurological syndromes and pain.
Another equally common cause is osteochondrosis. This disease is degenerative; during its development, the intervertebral discs are primarily affected, which first lose their shock-absorbing properties, bulge and begin to become overgrown with bone growths. It is these growths that cause compression of the nerve roots, and, accordingly, the cause of pain.
Spondylosis is not a very common problem, but it is this disease that leads to compression of the nerve endings that form the sciatic nerve.
When the sciatic nerve hurts, the cause may not be neuralgia of the nerve itself, but piriformis syndrome. It should be noted that this nerve is located just behind it. Pain in this case appears due to stretching or irritation of the nerve by the muscle itself. The pain is absolutely the same as with sciatica.
Pain due to inflammation of the sciatic nerve can also be observed if the functioning of the sacroiliac joint is disrupted. A nerve root runs next to it, so joint problems can cause pain.
This, unfortunately, is not all possible reasons. For example, sometimes the sciatic nerve hurts during pregnancy, as well as with a number of serious diseases - abscess, tumor, fibromyalgia, Lyme disease, etc.
How does sciatica manifest itself?
It is worth noting that the severity of symptoms of sciatica can vary in severity. In some patients the pain is intense, in others it is mild, but may increase over time or with certain movements. In this case, as a rule, pain is present only on one side. Depending on how much of the nerve root is affected, the pain may spread throughout the entire leg and all the way to the toes. Often pain syndrome is accompanied by neurological disorders, numbness, for example.
The most common symptoms are:
- pain due to inflammation of the sciatic nerve (including constant pain), which is localized in the back of the leg and can intensify when a person is in a sitting position;
- numbness, weakness and difficulty moving in the affected leg;
- tingling or burning in the lower leg;
- shooting pain that makes it difficult to stand for long periods of time.
It is also worth noting that very often in such a situation, back pain is often much weaker than the pain felt in the leg. In general, the severity of symptoms depends on how severely the nerve roots are affected.
 In order to assess the complexity of the disease, it is necessary to undergo an MRI examination of the lumbosacral spine.
In order to assess the complexity of the disease, it is necessary to undergo an MRI examination of the lumbosacral spine.
Among the numerous problems associated with the lower extremities, one should highlight the situation when the legs go numb. A general practitioner hears such complaints almost every day, not to mention more specialized specialists. And this brings nothing to patients except inconvenience and anxiety about their health. In order to get rid of similar sensations, you should first find out their cause and do everything exactly as the doctor recommends.
Causes
The most common numbness in the legs is below the knees. This is due to the fact that the legs and feet, firstly, are subject to significant load, bearing the weight of the whole body, and secondly, they are as far as possible from the central organs of the vascular and nervous systems. Such conditions create the prerequisites for the development of conditions that are characterized not only by local disturbances, but also by damage at a distance. These include:
- Polyneuropathy.
- Vascular diseases.
- Spinal diseases.
- Tunnel syndromes.
- Pathology of the spinal cord and brain.
- Traumatic injuries.
- Tumors.
- Frostbite.
Thus, the problem may lie not only in the peripheral parts of the limbs, but also much higher - in the spine and even the head. You can find out why your legs go numb from the hip to the foot by carefully differential diagnosis, taking into account all conditions with a similar clinical picture.
The causes of numbness in the legs are quite diverse; the same symptom can indicate a completely different pathology.
Symptoms
To determine the symptoms of the disease, the doctor conducts a clinical examination. It includes subjective information received from the patient (complaints), as well as objective data revealed during examination. All symptoms are subjected to maximum detail and subsequent analysis in order to form a holistic view of the disease.
Unpleasant symptoms can be felt in various parts of the limb: thigh, lower leg or foot. Their localization will often tell a lot about the location of the main pathological focus. However, numbness in the legs is unlikely to be the only sign of pathology - most often there are other manifestations, sometimes more significant.
Polyneuropathy

A common cause of numbness in the legs below the knee is polyneuropathy. In most cases, it occurs due to metabolic disorders in the body (with diabetes mellitus, diseases thyroid gland, renal failure, various intoxications). Disorders are not limited to numbness, but include the following symptoms:
- Moderate to intense pain in the legs and feet.
- A crawling sensation, a burning sensation.
- Reduced surface sensitivity.
- Changes in reflexes.
In addition to the lower extremities, nerves in other parts of the body may be affected, since the process is multiple. Polyneuropathy necessarily occurs against the background of an underlying disease, which has its own characteristic features.
If your legs below the knees are numb, then first of all it is necessary to consider the issue of multiple nerve damage - polyneuropathy.
Vascular diseases

Numbness in the legs from the hip to the foot can be the result of vascular problems. It takes a long course of the disease for sensory disturbances to develop, so acute conditions not worth keeping in mind. As a rule, such a symptom is considered as a sign of endarteritis, atherosclerosis or varicose veins of the lower extremities. Along with it, the following complaints can be noted:
- Feeling tired in the legs in the evening.
- Pain in the calf muscles when walking is a symptom of “intermittent” claudication.
- Pale or bluish skin, dilated saphenous veins.
- Reduced pulsation in various areas of the main arteries: on the foot and above - under the knee, in the thigh area.
- Trophic disorders: hair loss, formation of ulcers.
In most cases, there is bilateral damage to the arteries or veins. If you do not pay attention to the signs of the disease in time, especially with endarteritis and atherosclerosis, you will have to expect a significant increase in ischemia, which in the future can cause gangrene.
When symptoms of vascular pathology of the lower extremities appear, in order to avoid complications, you should consult a doctor in time.
Spinal diseases
The cause of numbness in the lower extremities often lies in diseases of the lumbar region - osteochondrosis or disc herniation. In this case, compression of the spinal roots that give rise to the sciatic nerve occurs, which is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Pain in the lower back, radiating to the leg - buttock, back of the thigh, lower leg and foot.
- Other sensory disorders.
- Feeling of weakness on the affected side.
- Limitation of lumbar mobility.
Compression of the root most often occurs on one side, but damage to both nerves is possible. Upon examination, tension in the back muscles and pain in the paravertebral points are revealed. Therefore, when your leg goes numb, you must definitely pay attention to the condition of the spine.
Tunnel syndromes

If numbness in the legs occurs in a specific area, then we can assume compression of the corresponding nerve in the canal formed by bones, tendons and muscles. This is observed at various levels, starting from the inguinal fold and is provoked by injuries, hematomas, and tumors.
When your right leg goes numb outer surface hips above the middle suggests Roth's disease. In other words, it is neuropathy of the external cutaneous nerve, which is located very superficially and can be compressed by a belt or objects located in pockets. Only local sensory disorders are characteristic. Numbness on the inside of the leg indicates damage to the femoral nerve. At the same time, movement disorders are also observed:
- Weakening of the knee reflex.
- Weakness and wasting of the quadriceps and iliopsoas muscles.
- Impaired hip and knee flexion.
And if, for example, the left leg goes numb on the outside of the shin and along the dorsum of the foot, then you need to think about compression of the peroneal nerve. Patients complain of pain in the legs below the knee, crawling “goosebumps”. The extension of the foot and fingers is impaired, causing walking to suffer.
Any numbness in the lower extremities should be considered a sign of pathology, the nature of which must be determined by the doctor.
Treatment
Once it becomes known why the patient’s legs are numb, treatment should be started immediately. First of all, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of this condition, be it compression of a nerve, occlusion of a vessel, or a violation of metabolic processes in the body. Only after the elimination of the main pathological process can we talk about the restoration of sensitivity in certain parts of the lower limb.
Drug therapy
In most cases, the disease that causes numbness in the legs is treated with medication. The doctor selects the optimal drugs that are indicated for the identified pathology, and the patient only needs to follow his recommendations. Depending on the clinical situation, the following medications may be used:
- Anti-inflammatory (Ortofen, Larfix).
- Muscle relaxants (Mydocalm).
- Vitamins (Milgamma).
- Antiplatelet agents (Aspecard).
- Venotonics (Detralex).
- Antioxidants (Cytoflavin, Berlition).
- Vascular (Actovegin, Latren).
Treatment will be more effective if it is carried out in stages - first using injectable forms of drugs, and then tablets.
Physiotherapy

Physiotherapy methods help improve nerve conduction and blood circulation. Such treatment includes local and general procedures, which are carried out under the supervision of a specialist. For numbness in the extremities above or below the knees, the following methods may be indicated:
- Electrophoresis.
- Magnetotherapy.
- Wave treatment.
- Barotherapy.
- Reflexology.
- Spa treatment.
The physiotherapist will create an optimal program consisting of the most effective procedures. In combination with other methods, this will be a good impetus for recovery.
Physiotherapy

When the left leg goes numb after an injury or similar symptoms appear due to osteochondrosis, certain therapeutic exercises, which will restore not only the motor function of the limb, but also help normalize sensitivity. You need to do gymnastics regularly, starting in a hospital setting and under the supervision of a doctor, and continuing at home. But such exercises are justified only after the pain syndrome has been eliminated.
Operation
In some cases, adequate treatment is only possible through surgery. This happens with serious injuries, severe vascular pathology, tumors, and intervertebral hernias. The main goal of surgery is to eliminate pathological formations that cause compression of nerve fibers or disruption of blood flow through the vessels. Recently, endoscopic and microsurgical techniques have been used, which are less traumatic compared to open operations and do not require long recovery.
If there is numbness in the lower extremities, you should first find out why this symptom appears. A correct diagnosis allows you to effectively treat the disease, which gives hope for a speedy recovery.
Pain in the legs from the knee to the foot: why do the legs hurt below the knees?
Severe pain in the legs bothers almost every second person. The discomfort most often affects the lower extremities.
The causes of the problem may lie in banal fatigue after a long walk, physical activity or uncomfortable shoes.
However, sometimes the legs below the knees and bones hurt due to the development of articular pathology, for which timely treatment cannot be ignored.
Features of the structure of the legs and causes of pain
If a person suffers from pain in the legs below the knees, then usually we are talking about the area from the lower leg to the foot. The lower leg consists of the fibula and tibia, nerve, venous, arterial fibers, and a large number of muscles.
If there is discomfort of an organic or functional nature, the pain syndrome will radiate to the lower leg. In some cases, pain is not critical and may not be a threat to health. There are pathological conditions when pain below the knee becomes life-threatening for the patient. For example, this is relevant for deep vein thrombosis.
In such situations, you cannot delay treatment, because if a blood clot has formed in the legs, then in the absence of diagnosis and when treatment is not started, the clot may break off. This causes blockage pulmonary artery and instant death.
Only a doctor who can prescribe adequate treatment can answer the question of why the legs hurt below the knees. Often the causes of pain in the muscles and bones of the limbs lie in:
- muscle tone, spasms caused by prolonged stress on the leg (physical strain);
- injuries (sprains, torn ligaments, muscles, bone fractures);
- inflammatory process in the lower leg (myositis);
- varicose veins of the legs;
- atherosclerosis (plaques in the arteries);
- arthrosis, arthritis;
- osteoporosis;
- thrombosis of deep veins, vessels and arteries below the level of the knees;
- osteomyelitis (infection of the inside of the legs);
- diseases of rheumatic nature;
- polyneuropathy (pathology of nerve fibers) in patients with diabetes, chronic smokers and alcoholics;
- lymphostasis of the vessels of the leg;
- diseases of the leg arteries (vasculitis, periarthritis nodosa);
- compression of the soft tissues of the extremities;
- benign and malignant tumors bones, muscles, tissues below the knees;
- lack of microelements in the blood (magnesium, potassium, calcium);
- prolonged use of medications (diuretics, glucocorticosteroids);
- compression of nerve endings, for example, with osteochondrosis.
Varicose veins and vascular thrombosis
Pain below the knee can be caused by varicose veins. The disease manifests itself as enlarged veins in the legs, and in the initial stages this symptom is not visible. Other signs of varicose veins will be swelling of the legs at the end of the day, a burning sensation and heaviness, rare cramps, a dull aching pain that goes away after resting in a horizontal position.
This pathology can develop in a fairly short period of time, is acute and is usually accompanied by vivid external manifestations. Varicose veins in some cases occur with blockage of arteries or veins.
With venous thrombosis, symptoms appear gradually over a couple of days. In this case, the patient suffers from heaviness in the legs and excruciating arching pain.
The pain is localized as outside limbs and internal:
- legs swell (immediately left and right);
- the skin on them becomes very red.
In the hearth inflammatory process the temperature rises, the leg becomes hot. After some time, the redness gives way to a bluish color. The pain syndrome in a person is so severe that he is unable to step on the affected limb. Already on days 3-4, tissue death and gangrene occur. If there is no treatment or it is not timely, the patient risks losing the affected leg or dying.
With arterial thrombosis, the affected leg becomes numb and cold within a few hours. Due to the fact that the lower leg is left without blood supply, its covers become white.
In addition, sudden, quite acute pain below the knee may appear. Without medical intervention, tissues die within 2-4 hours due to necrosis.
Mineral deficiency, polyneuropathy, polyarthritis obliterans
If there is a lack of any microelements in the body, pain in the legs may develop. There are many reasons for this, for example, bones do not receive the required amount of calcium. In this case, cramps in the calf muscles may develop, especially at night. Because of this, the patient is unable to fully rest.
The attacks last several minutes and go away on their own. You can make your well-being easier by massaging the affected area of your leg.
With polyneuropathy of the lower extremities, the causes of pain in the left leg usually lie in diabetes mellitus. The disease affects not only vital organs, but also bones and nerve endings. Sometimes diabetes makes itself felt by severe pain in the muscles and bones around the foot. This is especially true for type 2 pathology.
Signs of polyneuropathy:
- burning pain in front of leg;
- numbness and the so-called cold extremity syndrome.
It hurts constantly, and the intensity of the discomfort does not depend on physical activity and type of activity.
When the leg muscles hurt due to obliterating polyarthritis, the patient suffers from a disruption of the main blood flow in the legs, caused by a narrowing of the lumen of the blood vessels. The causes of the pathology are the development of atherosclerotic plaques.
The person feels pain from the knee to the foot and is forced to limp. Often, discomfort in the front of the legs occurs when walking for a long time, especially over long distances. If you rest for at least a few minutes, the pain syndrome subsides.
In cases where it is not provided health care, the disease is actively progressing, the pain intensifies and reduces the muscles of the left and right legs even at rest. Trophic ulcers form on the skin of the legs, the integument peels off and becomes too dry. In addition, the nail plates on the left and right legs are connected to the pathological process.
This disease can cause the affected limb to die due to gangrene. If your legs hurt from the knee to the foot, then it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination and begin appropriate treatment.
Preventive measures and pneumopressotherapy of the legs
To prevent the development of leg pathologies and pain syndrome, you should consult a doctor. They will tell you how to protect yourself and what you absolutely should not do. So, to prevent restless legs syndrome, you should follow these simple recommendations:
- Avoid wearing uncomfortable, tight clothing, especially trousers. This will help prevent venous and lymphatic congestion in the legs, especially in the front;
- correct flat feet;
- when sitting for a long time, avoid a position where the left leg is crossed over the right, as this compresses the blood vessels;
- control water-salt balance;
- during rest, it is better to lie on your back, while raising your legs up for at least half an hour to improve blood supply to the muscles;
- bring your weight to normal;
- take walks as often as possible;
- walk barefoot on uneven surfaces;
- dilute a sedentary lifestyle with regular exercise and sports;
- carry out exercises for the foot, lifting small objects from the floor with your left and right feet. The exercise develops the muscles in the front of the limb well.
Pneumopressotherapy is an excellent way to stop or prevent leg problems. This physiotherapeutic treatment has a beneficial effect on the body and tissues of the legs by displacing venous blood from muscle pockets, where lymph often stagnates.
Using a special medical device, a foot massage is performed, during which the effect on the tissue is dosed. One pneumopressotherapy procedure can replace about 30 sessions of standard manual massage.
In addition, such preventive treatment has a positive effect on appearance legs, especially if the procedure is done systematically.
What is sciatica and why is this disease dangerous?
 Sciatica is a complex disease characteristic symptoms which are pain, periodic tingling, weakness and numbness that occurs along the sciatic nerve from the lower back and buttocks to the legs and thighs. Today we will tell you what this disease is and how it can be cured.
Sciatica is a complex disease characteristic symptoms which are pain, periodic tingling, weakness and numbness that occurs along the sciatic nerve from the lower back and buttocks to the legs and thighs. Today we will tell you what this disease is and how it can be cured.
- Sciatica: what kind of disease is it?
- Why does sciatica appear?
- Symptoms of sciatica
- Types of diagnostics for sciatica
- Features of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- How to treat sciatica?
- Features of massage for sciatica
- Effect of acupuncture for sciatica
- The use of osteopathy for sciatica
- Therapeutic exercises during sciatica
- Treatment of sciatica with traditional methods
- Preventive measures against sciatica
Sciatica: what kind of disease is it?
The sciatic nerves are the longest in our body. Each spinal root begins on a five-level segment of the lumbosacral region. Each descends down the legs and branches along the way, supplying small nerve processes with such parts of the body as:
- shins;
- hips;
- knees;
- fingers;
- feet.
Since the sacral spine bears the key load, then for all lesions that can cause pinching, compression or irritation of the trunk of the sciatic nerve or its roots. Pain can spread to all areas of the body along the path of the main trunk.
Why does sciatica appear?
The causes of this disease are as follows:

Symptoms of sciatica
The only symptom of this disease is often pain. It has the following features:
- dagger, shooting and burning character;
- spread to the buttocks, back of the thighs, back of the lower legs and popliteal fossa. They can spread throughout the leg and reach the tips of the fingers, sometimes it appears in the lower back;
- With this disease, pain is most often chronic. They may be constant or intermittent;
- they can vary in strength, be either too intense and cause severe suffering, or not very intense and do not cause discomfort;
- Most often, with sciatica, the pain is unilateral - appearing on only one side, in rare cases - on both sides at once.
With a disease such as sciatica, the following neurological disorders appear:

Types of diagnostics for sciatica
Sciatica is a disease that requires diagnosis, which can be different and has its own advantages and contraindications.
X-ray. Radiography during sciatica allows you to diagnose this disease, which is a consequence of vertebral pathologies and intervertebral discs. It's a quick and easy way to diagnose sciatica, and it's affordable.
X-rays should not be taken in the following cases:
- during pregnancy;
- with severe anxiety, when it is impossible to record a person’s movements;
- with severe obesity, when the vertebrae cannot be seen in the picture.
Computed tomography as a method for diagnosing sciatica can reveal the true causes of pain in the sciatic nerve. Unlike radiography, tomography is more informative and accurate; it also helps to construct layer-by-layer sections of the lumbar spine or its 3-D model.
Like x-rays, tomography cannot be prescribed during pregnancy and in a number of other cases, provided individually. This research method does not allow us to examine in detail only soft tissues:
- muscles;
- nervous tissue and others.
Features of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
 This type of tomography has the same capabilities as computer tomography, and not only:
This type of tomography has the same capabilities as computer tomography, and not only:
- layer-by-layer images of the body are obtained;
- a clear 3-D image of the spinal column, intervertebral disc and spinal cord is constructed;
- the ability to obtain a clearer image of soft tissues.
MRI is very effective method diagnosing the causes of sciatica, using it to investigate:
- spinal cord;
- membranes of the spinal cord;
- roots;
- vessels;
- adjacent tissues.
Indications for this type of diagnosis are:
- the presence of a pacemaker is a device that is sewn into the heart muscle during arrhythmia;
- the presence of a metal implant in the middle ear that can be magnetized;
- the presence of any metal implants capable of magnetization, metal fragments remaining after wounds and injuries;
- artificial mechanical ventilation of the patient's lungs;
- the presence of the Ilizarov apparatus is a metal device for connecting and holding bones in place after fractures.
- Thanks to MRI, it is possible to identify the causes of sciatica located in the following places:
- nerves;
- muscles;
- other soft tissues that are not visible on images of other types of diagnostics.
Sciatica is also diagnosed through electroneuromyography, which is performed on some sciatica sufferers to evaluate nerve conduction if sensation and motor ability are impaired. Special electrodes are placed on the muscles to record the passage of nerve impulses.
How to treat sciatica?
There are different areas of treatment for a disease such as sciatica:

We will describe in detail below some methods of treating this disease.
Features of massage for sciatica
With this disease, and as in acute stage, and during remission massage is used. The rules for its implementation in the presence of sciatica are as follows:
- in the presence of lumbosacral radiculitis, which affects the sciatic nerve, they practice massage of the lower back, buttocks, back of the thigh, feet and legs;
- in the acute phase of this disease, rubbing and stroking are used, but vibration and kneading only intensify the pain;
- when pain and other symptoms subside, the massage will be more intense; you can practice acupressure, cupping and reflex-segmental massage;
- essential oils during massage improve its effect;
- for sciatica, massage is best combined with rubbing with ointments and special gymnastics;
- one massage session lasts about half an hour;
- total number of sessions – 10.
For sciatica, massage has the following effect:
- distracting and annoying;
- blood flow to the affected roots and nerves is better;
- increased muscle tone, which is caused by pain, is relieved;
- inflammatory swelling is relieved, lymph outflow is improved;
- biologically excreted in the skin active substances, reducing inflammation and pain.
Effect of acupuncture for sciatica
 Acupuncture is effectively practiced for sciatica and different forms radiculitis, however, not much research has been carried out in this regard.
Acupuncture is effectively practiced for sciatica and different forms radiculitis, however, not much research has been carried out in this regard.
The procedure looks like this: at some points, thin needles based on stainless steel or precious materials are inserted into the skin. It should only be performed by a qualified specialist.
The effects of this treatment method are as follows:
- pain relief occurs due to the release of endorphins - these are natural substances that act in a similar way to analgesics;
- the protective forces and regenerative abilities of tissues increase;
- small vessels dilate and blood flow improves, the condition of pinched roots improves;
- general inflammation and edema goes away.
Contraindications to the use of this technique are:
- presence of cancer;
- acute infections;
- skin damage at the affected areas.
A course of acupuncture treatment for sciatica lasts about three months. At first it lasts 3-4 sessions per week, and then it is from 1 to 4 courses per month.
The use of osteopathy for sciatica
Osteopathy is a modern direction in the treatment of sciatica and a number of other diseases. It is a small application of pressure and movement that helps eliminate inflammation and pain.
This method has virtually no contraindications. And the positive effect is achieved after the first session. This method does not deal with the cause of the disease, but only relieves the symptoms of sciatica.
Therapeutic exercises during sciatica
In the acute stage of sciatica, the patient is prescribed bed rest and any physical activity is prohibited. He is placed on his back, his legs are raised on a platform, and pillows are placed under his lower back.
When the pain subsides, the following exercises are prescribed:
- lying on your back, pull your legs bent at the knees to your chest. Repeat the exercise 10 times;
- lying on your stomach, lift your body as if doing a push-up and repeat 5 times;
- lying on your back, raise your legs straight up and hold for 5 minutes;
- sitting on your knees, lean forward, raising your arms up, and clasp your hands;
- in a standing position, place your feet shoulder-width apart, bend alternately to the right and left.
All exercises should be done gently and carefully, since sciatica can appear at any time.
Treatment of sciatica with traditional methods
Below are recipes for some folk remedies for sciatica.
So, to prepare a special infusion for pain, prepare the following ingredients:
- a tablespoon of viburnum;
- the same number of calendula flowers;
- the same amount of thyme herb;
- two large spoons of horsetail grass;
- 0.5 liters of water.
Grind everything prepared and take 2 large spoons of the resulting mixture. Bring to a boil and simmer for 5 minutes, then cool. You need to take half a glass three times a day before meals.
It is also recommended to practice rubbing with homemade agave. Cut off the stem of agave - this is a potted plant that can be purchased at a specialty store. The stem should not be too young or old, otherwise there will be no effect and the skin will burn. It needs to be cleared of thorns and cut lengthwise. Rub the cut into the area of pain 2-3 times a day.
Even with sciatica, you can rub the sore spot with homemade ointment. To prepare it you will need:
- 5 glasses of squeezed black radish juice;
- 1 glass of honey;
- 1 tablespoon table salt;
- a glass of vodka.
Mix all ingredients and shake the mixture well before each rub. Rub it on your lower back and back of your thighs twice a day.
And to make an effective compress for sciatica, grate a black radish, place a piece of cloth on your lower back, place the radish on top, and put another piece of cloth on top, then cover it with wax paper and wrap it in something warm. The compress is applied twice a day for 15 minutes.
Sciatica is also treated with methods such as:

In some cases, sciatica can be treated through surgery, but this is very rare.
Preventive measures against sciatica
The following methods of prevention are practiced against this disease:
- exercise fully, but not too intense. Brisk walking, yoga and swimming are best;
- maintaining hygiene at work;
- comfortable sleep - the bed should not be very soft, not very hard;
- Lift heavy things correctly.
Sciatica can be cured if diagnosed and chosen correctly the right way treatment. Prevention of this disease is also very important.